We Recommend:
Bach Steel - Experts at historic truss bridge restoration.
BridgeHunter.com Phase 1 is released to the public! - Visit Now
Old OH-522 Bridge

Primary Photographer(s): Nathan Holth and Rick McOmber
Bridge Documented: June 7, 2014
Rural: Lawrence County, Ohio: United States
By Builder/Contractor: Unknown
1990
50.0 Feet (15.2 Meters)
93.0 Feet (28.3 Meters)
17.7 Feet (5.39 Meters)
2 Main Span(s)
4432436

View Information About HSR Ratings
Bridge Documentation
View Archived National Bridge Inventory Report - Has Additional Details and Evaluation
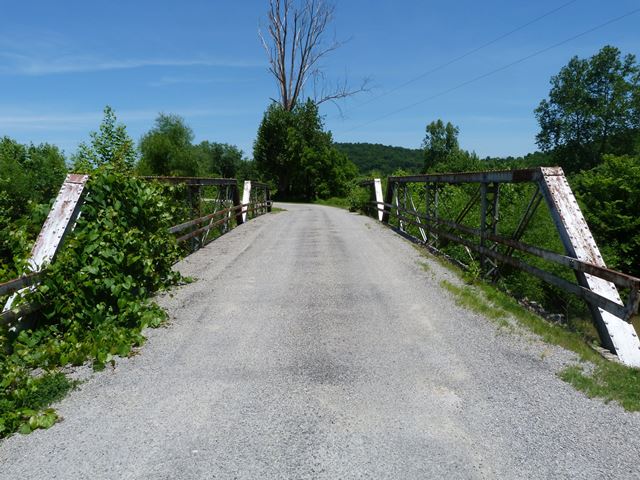
This bridge is an uncommon example of a multi-span pin-connected pony truss. It is traditionally composed and retains excellent historic integrity with no major alterations. The two spans are not identical. The northern span is shorter with only three panels and about 43 foot span, while the southern span has four panels and is about a 50 foot span.
The Historic Bridge Inventory suggested a ca. 1900 construction date for this bridge. HistoricBridges.org suggests the bridge is older, and dates anywhere from the 1880s up to 1895. The bridge has Carnegie brands on the metal, and the Carnegie name is presented in a plain, simple font with no styling. This brand usually appears on older trusses from the 1880s, although this font has been found on bridges as late as 1895 as shown on the Iron and Steel Brands page. Moverover, the riveted built-up floor beams on this bridge are further suggestive of a bridge from this period.
The National Bridge Inventory in contrast had a 1934 construction date listed. The concrete pier and abutments look like they date to this period. The trusses may have been relocated here from a different former location in 1934.
Information and Findings From Ohio's Historic Bridge InventorySetting/Context The bridge carries a 2 lane road over a stream in a sparsely developed, rural setting. Physical Description The 2 span, 93'-long, pin-connected Pratt pony truss bridge is traditionally composed of built-up compression members and eyebar or rod tension members. It is supported on abutments and piers with horizontal scoring. Integrity Floorbeams repaired/strengthened and new stringers/floor in 1990. BMS has year built of 1934, which is probably relocation date. Trusses are stylistically ca. 1900. Summary of Significance The ca. 1900 pin-connected Pratt pony truss bridge has no distinctive details or features. The not eligible recommendation of the prior inventory remains appropriate. The 1934 BMS year built may be a relocation date, as the substructure is definitely 1934 in appearance, but the trusses are clearly ca. 1900 by style. Pratt trusses were undoubtedly the most popular truss design of the last quarter of the 19th century and continued to be built into the 20th century, although eventually superseded in popularity by Warren trusses. The design, which initially was a combination of wood compression and iron tension members, was patented in 1844 by Thomas & Caleb Pratt. Ohio has three covered bridges that use this combination configuration, but they are all modern reconstructions based on the Pratt patent. The great advantage of the Pratt over other designs was the relative ease of calculating the distribution of stresses. More significantly, it translated well into an all-metal design in lengths of less than 200'. Significant surviving examples of all-metal Pratt trusses mostly date to the last quarter of the 19th century, and they are found with thru, pony, and the less common bedstead configuration. Prior to about 1890, a variety of panel point connections were in widespread use (including bolts, cast-iron pieces, and pins), but engineering opinion was coalescing around pins as the most efficient and constructible. Many of the connection details were proprietary and associated with individual builders or companies, and thus earlier examples are generally taken to be technologically significant in showing the evolution of the design. Later post-1890 Pratt trusses show a progression toward less variation in their details such that by 1900 the design was quite formulaic with few significant differences between the designs of various builders. This marked the end of the pin-connected Pratt's technological evolution and, in fact, it was soon waning and eclipsed in the highway bridge market by more rigid, rivet-connected truss designs, particularly the Warren but also riveted Pratts. The transition to riveted connections, which happened even earlier with railroads than highways, was in no small part due to concerns about stress reversals at the pins under heavier loads and improvements in pneumatic field riveting equipment in the early 1900s. In Ohio, Pratt truss highway bridges, whether pinned or riveted, were almost always built under the auspices of counties and local units of government; the Pratt was not a standard design of the state highway department. In Ohio, there are 185 Pratt trusses dating from ca. 1874 to 1945 with at least 60 dating prior to 1900 (Phase 1A, 2008). The technologically significant unaltered examples of pin-connected Pratt trusses for the most part date prior to 1900 and have documented or attributed builders and dates of construction and/or significant connection or member details. Later post-1900 examples are less technologically significant. Significant unaltered examples of riveted-connected Pratt trusses date from ca. 1900 to 1915. Bridge Considered Historic By Survey: No |
![]()
Photo Galleries and Videos: Old OH-522 Bridge
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Original / Full Size PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery offers photos in the highest available resolution and file size in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Mobile Optimized PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery features data-friendly, fast-loading photos in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Maps and Links: Old OH-522 Bridge
Coordinates (Latitude, Longitude):
Search For Additional Bridge Listings:
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers) of this bridge.
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 10 miles (16 kilometers) of this bridge.
Additional Maps:
Google Streetview (If Available)
GeoHack (Additional Links and Coordinates)
Apple Maps (Via DuckDuckGo Search)
Apple Maps (Apple devices only)
Android: Open Location In Your Map or GPS App
Flickr Gallery (Find Nearby Photos)
Wikimedia Commons (Find Nearby Photos)
Directions Via Sygic For Android
Directions Via Sygic For iOS and Android Dolphin Browser
USGS National Map (United States Only)
Historical USGS Topo Maps (United States Only)
Historic Aerials (United States Only)
CalTopo Maps (United States Only)