We Recommend:
Bach Steel - Experts at historic truss bridge restoration.
BridgeHunter.com Phase 1 is released to the public! - Visit Now
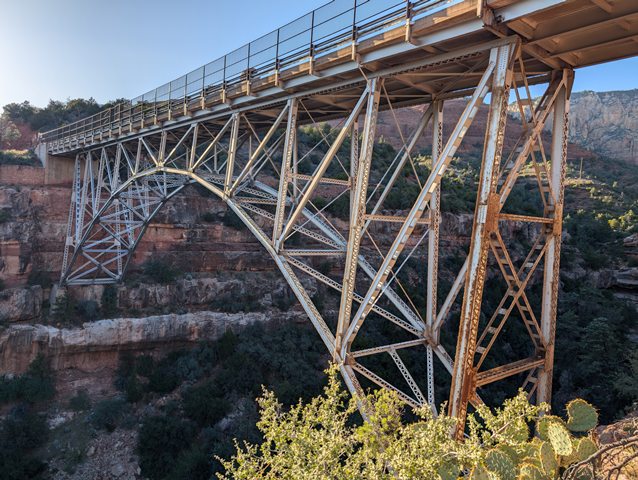
Midgley Bridge

Primary Photographer(s): Nathan Holth
Bridge Documented: September 17, 2024
Sedona: Coconino County, Arizona: United States
Metal Two-Hinged Solid Ribbed Spandrel Braced Deck Arch, Fixed and Approach Spans: Metal Continuous Stringer (Multi-Beam), Fixed
1938 By Builder/Contractor: Lewis Brothers of Phoenix, Arizona and Engineer/Design: US Bureau of Public Roads
Not Available or Not Applicable
240.0 Feet (73.2 Meters)
374.0 Feet (114 Meters)
Not Available
1 Main Span(s) and 3 Approach Span(s)
232

View Information About HSR Ratings
Bridge Documentation
Disclaimer: Generated with the aid of ChatGPT AI, the below narrative is based on sources provided by Nathan Holth and crafted to align with his research and passion for historic bridges.
History
Midgley Bridge is a historic deck arch bridge located near Sedona, Arizona, spanning Wilson Canyon along State Route 89A. The bridge was constructed in 1938-1939 as the final link in a major infrastructure upgrade of the Oak Creek Highway between Sedona and Flagstaff. The U.S. Bureau of Public Roads (BPR) initiated the project under Arizona Forest Project 7, dividing it into multiple contracts during the early 1930s. Midgley Bridge was the last component needed to complete the new roadway.
Designed by BPR engineers, the bridge was built by Lewis Brothers of Phoenix, Arizona. Construction began on March 24, 1938, with excavation for the arch pedestals in the canyon. The steel structure was completed by October 31, 1938, under the supervision of BPR Resident Engineer V.G. Watson. The bridge was named in honor of W.W. Midgley, a local rancher from the 19th century who contributed to the development of the region.
Since its completion, the bridge has remained largely unaltered except for the addition of modern steel thrie-beam railings attached to the original guardrails. It continues to serve as a vital link on US 89A, providing a scenic and historically significant crossing over Wilson Canyon.
Design
Midgley Bridge is a two-hinged, spandrel-braced steel deck arch with a total length of 374 feet (114 meters) and a main span of 240 feet (73.2 meters). The bridge’s design resembles a scaled-down version of the Navajo Bridge (1929), another prominent deck arch in Arizona.
Key structural elements include:
Arch Structure: The steel arch consists of two built-up box beams composed of twin channels with double lacing on the top and bottom.
Superstructure: The arch supports a reinforced concrete deck resting on a series of I-beam steel floor beams, which in turn are supported by W-beam and built-up columns.
Substructure: The bridge is anchored by reinforced concrete abutments and arch pedestals, with stone masonry wingwalls enhancing its visual appeal.
Deck and Guardrails: The deck width measures 27.2 feet (8.3 meters), with a roadway width of 24 feet (7.3 meters). The bridge originally had steel guardrails, later reinforced with modern thrie beams for improved safety.
The structure is functionally classified as a principal arterial (rural) and has a daily traffic count of approximately 3,858 vehicles as of 2016. It remains open with no restrictions but has been deemed functionally obsolete due to its outdated deck geometry.
Historic Significance
Midgley Bridge holds historical and engineering significance due to its rare deck arch configuration and its role in completing the Oak Creek Highway. While Arizona has numerous long-span steel arches, only the Navajo Bridge and Midgley Bridge feature spandrel-braced arches, making them unique among the state’s historic bridges.
The bridge is considered potentially eligible for the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) due to its association with:
Transportation History: It served as the final connection between Sedona and Flagstaff, enhancing regional mobility and economic development.
Engineering and Design: It represents a well-preserved example of an esoteric and dramatic structural type that was uncommon in the region.
Scenic and Cultural Importance: Located in a striking natural setting, Midgley Bridge contributes to the historic and aesthetic landscape of Arizona’s red rock country.
The Midgley Bridge remains an important regional landmark and a testament to early 20th-century bridge engineering in Arizona.
View Archived National Bridge Inventory Report - Has Additional Details and Evaluation
View Historic Bridge Inventory Sheet For This Bridge
![]()
Photo Galleries and Videos: Midgley Bridge
Unorganized Photos
Original / Full Size PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos, presented as an unorganized and unlabeled collage and gallery. This gallery offers photos in the highest available resolution and file size in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Unorganized Photos
Mobile Optimized PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos, presented as an unorganized and unlabeled collage and gallery. This gallery features data-friendly, fast-loading photos in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Maps and Links: Midgley Bridge
Coordinates (Latitude, Longitude):
Search For Additional Bridge Listings:
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers) of this bridge.
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 10 miles (16 kilometers) of this bridge.
Additional Maps:
Google Streetview (If Available)
GeoHack (Additional Links and Coordinates)
Apple Maps (Via DuckDuckGo Search)
Apple Maps (Apple devices only)
Android: Open Location In Your Map or GPS App
Flickr Gallery (Find Nearby Photos)
Wikimedia Commons (Find Nearby Photos)
Directions Via Sygic For Android
Directions Via Sygic For iOS and Android Dolphin Browser
USGS National Map (United States Only)
Historical USGS Topo Maps (United States Only)
Historic Aerials (United States Only)
CalTopo Maps (United States Only)