We Recommend:
Bach Steel - Experts at historic truss bridge restoration.
Narrowsburg Bridge

Primary Photographer(s): Nathan Holth and Rick McOmber
Bridge Documented: May 29, 2010
Hansdale and Delaware Turnpike (Beach Lake Highway / PA-652) / NY-52 (CR-24, Bridge Street) Over Delaware River
Darbytown and Narrowsburg: Wayne County, Pennsylvania and Sullivan County, New York: United States
Not Available or Not Applicable
290.0 Feet (88.4 Meters)
426.0 Feet (129.8 Meters)
26 Feet (7.92 Meters)
1 Main Span(s) and 2 Approach Span(s)
63065202501844

View Information About HSR Ratings
Bridge Documentation
View Archived National Bridge Inventory Report - Has Additional Details and Evaluation
Overview of Bridge
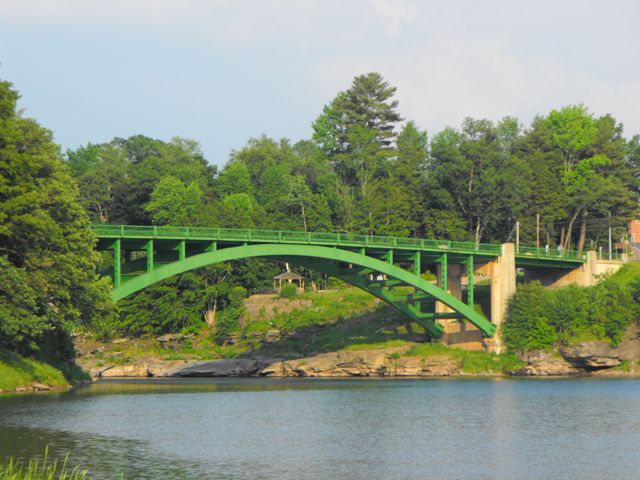
Constructed in 1954, this is a relatively young bridge in terms of considering it historic, however its design clearly harkens back to an area that has been forever lost in a modern world of pre-stressed concrete slabs with no aesthetic value whatsoever. In stark contrast, this riveted steel arch provides a graceful arch span over the Delaware River, providing a structure of both function and beauty. The bridge's arch is composed of built-up beams, but no v-lacing or lattice are present, which was the trend for the period in which this bridge was built. The arch springs from massive concrete piers that extend above the deck to form posts for the original metal railings which remain on the bridge. The arch span is flanked by a steel stringer approach span at each end. The abutments and the railings upon them are slightly flared.
Particularly in the eastern half of the United States, steel deck arch bridges are a very uncommon bridge type and were built in limited quantities, having been more common in the steep canyons and gorges that are more prevalent in the western United States. New York State was one state that built a fair number of steel deck arches however. In contrast, Pennsylvania rarely built steel deck arch bridges, the concrete arch bridge being far more common. This being the case, the Narrowsburg Bridge seems more a part of the context and history of New York than Pennsylvania.
History of Crossing
Narrowsburg gets its name from how the Delaware River becomes narrow between two rocky areas on each side of the river. It was originally sometimes called Big Eddy. The Erie Railroad originally crossed the river at Narrowsburg. The current Narrowsburg Bridge is only one of a number of preceding highway bridges at this site. The first couple bridges were of wood and did not last long, being washed away by floods in 1832 and 1846. One wood bridge did last a while, and was not replaced until 1899, when an iron bridge, likely a truss bridge, was constructed. The book Bridges Over the Delaware River lists the builder as the Oswego Bridge Company, although it is likely the actual name is the well-known Owego Bridge Company, a company that was regionally very prolific, with Narrowsburg being well within the company's radius of activity. The 1899 span was replaced by the current bridge. The current Narrowsburg Bridge was constructed by the New York-Pennsylvania Interstate Bridge Commission for $489,674. Its opening was celebrated at an event held at Peggy Runway Lodge. Soon after its completion, the Wayne County Turnpike and the Mount Hope-Lumberland Turnpike were completed and connected to the bridge.
Bibliography: Dale, Frank T. Bridges Over the Delaware River: A History of Crossings. Piscataway: Rutgers University Press, 2003.
Information and Findings From Pennsylvania's Historic Bridge InventoryDiscussion of Bridge The main span of the 426' long bridge built in 1954 is a 280'-long hingeless steel arch. The approach spans are stringers. The reinforced concrete piers and abutments are set on solid rock. The arch ribs are built up box section as are the spandrel columns. The bridge, built by the New York-Pennsylvania Interstate Bridge Commission, is a late example of a technology that was used in Pennsylvania since the late 19th century. The bridge is not historically or technologically significant. Discussion of Surrounding Area The bridge carries a 2 lane state highway over a stream in a sparsely developed, forested setting. The bridge is in the Upper Delaware River National Scenic and Recreation Area. The 19th and and early 20th century town of Narrowsburg, New York is adjacent to the bridge. The bridge is considerably newer than the character of its setting. Bridge Considered Historic By Survey: Not in Pennsylvania, Status in New York Unknown |
![]()
Photo Galleries and Videos: Narrowsburg Bridge
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Original / Full Size PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery offers photos in the highest available resolution and file size in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Mobile Optimized PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery features data-friendly, fast-loading photos in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Maps and Links: Narrowsburg Bridge
Coordinates (Latitude, Longitude):
Search For Additional Bridge Listings:
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers) of this bridge.
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 10 miles (16 kilometers) of this bridge.
Additional Maps:
Google Streetview (If Available)
GeoHack (Additional Links and Coordinates)
Apple Maps (Via DuckDuckGo Search)
Apple Maps (Apple devices only)
Android: Open Location In Your Map or GPS App
Flickr Gallery (Find Nearby Photos)
Wikimedia Commons (Find Nearby Photos)
Directions Via Sygic For Android
Directions Via Sygic For iOS and Android Dolphin Browser
USGS National Map (United States Only)
Historical USGS Topo Maps (United States Only)
Historic Aerials (United States Only)
CalTopo Maps (United States Only)