We Recommend:
Bach Steel - Experts at historic truss bridge restoration.
BridgeHunter.com Phase 1 is released to the public! - Visit Now
Cove Road Bridge
Bridge E-61

Primary Photographer(s): Marc Scotti
Bridge Documented: January 4, 2011
Rural: Oneida County, New York: United States
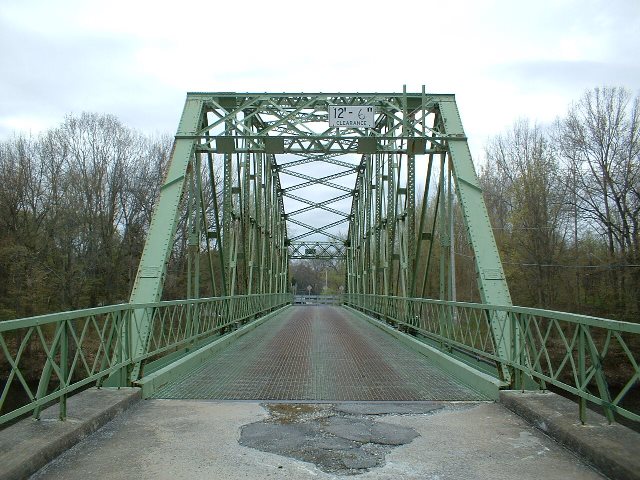
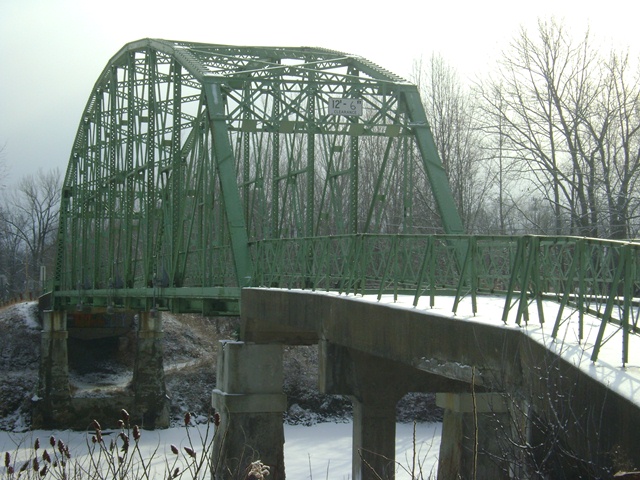
Metal 10 Panel Rivet-Connected Parker Through Truss, Fixed and Approach Spans: Concrete Slab, Fixed
1908 By Builder/Contractor: Groton Bridge Company of Groton, New York
1955
183.7 Feet (56 Meters)
302.8 Feet (92.3 Meters)
15 Feet (4.57 Meters)
1 Main Span(s) and 4 Approach Span(s)
4426090

View Information About HSR Ratings
Bridge Documentation
View Archived National Bridge Inventory Report - Has Additional Details and Evaluation
Most of the fixed bridges built ca 1910-1912 for the Erie Canal were Double-Intersection Warren through truss bridges. This bridge is a rare example of a fixed bridge that was built with a longer than normal span and a Parker truss span to accommodate it. This bridge, built in 1908, is also older than most of the truss bridges over the Erie Canal. It also has four approach spans instead of the more common two. This bridge's top chord substitutes the common use of cover plate for the less common use of lattice, a rare detail that adds a more open, geometric detail to this bridge not found on most bridges. The steel on this bridge bears the name "Jones and Laughlins" and the presence of the "s" in "Laughnlins" would indicate that the steel itself may date to before 1905. This bridge is among the most significant of the fixed Erie Canal truss bridges.
![]()
Historic Bridges of the New York State Barge Canal including the Erie Canal and Other Canals and Waterways
The Erie Canal is one of the most famous and historically significant canals in the United States. Aside from the widely recognized historical significance of the canal as a transportation facility itself, a lesser known fact is that the canal is historically significant for the bridges that have spanned the canal over the years. It was here on the Erie Canal where Squire Whipple found a place to successfully get his "Whipple Arch" bowstring truss bridges constructed in significant quantities in the mid-1800s. The success of his Whipple Arch bridges helped contribute to the nationwide transition from wooden bridges to metal bridges. The period of time from 1905-1918 where the Erie Canal was upgraded and widened to become part of the larger New York State Barge Canal was a time of change for the bridges of the canal. Between the process of widening and upgrading the canal, and the nationwide trend to build more substantial bridges in the early 20th Century, the previous generation of bridges (many undoubtedly those Whipple Arch bridges) were replaced by a series of new bridges. These bridges have proved to be very durable and thanks to a clear commitment to preservation on the part of New York State Department of Transportation and other agencies, the Erie Canal and the New York State Barge Canal system, particularly the western section from Lockport to Spencerport boasts one of the highest densities of historic bridges of any waterway in the country. The vast majority of bridges on this section are maintained in beautiful condition.
Although the new bridges from the early 20th Century took a variety of forms, two forms were by far the most common. In rural or spacious areas, a fixed double-intersection Warren through truss was used, with a dirt approach providing the modest elevation needed for a fixed bridge over the canal. Double-intersection Warren truss bridges are generally considered an uncommon truss type on a nationwide basis. In urban and less spacious areas, a vertical lift bridge was used. The vertical lift bridges are an unusual design. Instead of towers that rise above the bridge in a traditional vertical lift bridge and pull the truss span up using cables, these bridges have vertical endposts which extend below the deck and into the ground. When operated, these extended endposts (called the lifting frame) rise out of the ground. In an engineering sense, these unusual vertical lift bridges might be thought of as bedstead truss bridges. Another unique feature of these lift bridges are the stairways found at each end of the bridge on the sidewalks. These stairways allow pedestrians to continue to cross the bridge when the structure is in the raised position. These vertical lift bridges continue to operate for boats today, so observing these unique bridges remains possible.
Elsewhere, the New York State Barge Canal System boasts other types of historically significant bridges.
View National Register of Historic Places Nomination Form for the New York State Barge Canal (Alternate ZIP Version In Sections) - Note this impressive document contains modern color photos of the bridges, some from unique angles, historical photos showing bridge construction, and original plan sheets for some bridges too.
View a HistoricBridges.org photo gallery of the historical photos, modern photos, and original plans contained in the National Register Nomination. This photo gallery can also be found in the Fairport Bridge's page.
View Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) Overview of Erie Canal Locks at Lockport, NY (Data Pages)
View Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) Index - Has a list of structures including bridges that were individually documented for HAER.
Erie Canalway National Heritage Corridor
Annual Reports on the New York State Barge Canal (Order By Fiscal Years): 1908, 1909, 1910, 1911, 1912, 1913, 1914, 1915, 1916, 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921
Story of the New York State Canals (1916)
New York State Barge Canal (1915 Overview of Project)
This bridge is tagged with the following special condition(s): Unorganized Photos
![]()
Photo Galleries and Videos: Cove Road Bridge
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Original / Full Size PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery offers photos in the highest available resolution and file size in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Bridge Photo-Documentation
Mobile Optimized PhotosA collection of overview and detail photos. This gallery features data-friendly, fast-loading photos in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Additional Unorganized Photos
Original / Full Size PhotosA supplemental collection of photos that are from additional visit(s) to the bridge and have not been organized or captioned. This gallery offers photos in the highest available resolution and file size in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Additional Unorganized Photos
Mobile Optimized PhotosA supplemental collection of photos that are from additional visit(s) to the bridge and have not been organized or captioned. This gallery features data-friendly, fast-loading photos in a touch-friendly popup viewer.
Alternatively, Browse Without Using Viewer
![]()
Maps and Links: Cove Road Bridge
Coordinates (Latitude, Longitude):
Search For Additional Bridge Listings:
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers) of this bridge.
Bridgehunter.com: View listed bridges within 10 miles (16 kilometers) of this bridge.
Additional Maps:
Google Streetview (If Available)
GeoHack (Additional Links and Coordinates)
Apple Maps (Via DuckDuckGo Search)
Apple Maps (Apple devices only)
Android: Open Location In Your Map or GPS App
Flickr Gallery (Find Nearby Photos)
Wikimedia Commons (Find Nearby Photos)
Directions Via Sygic For Android
Directions Via Sygic For iOS and Android Dolphin Browser
USGS National Map (United States Only)
Historical USGS Topo Maps (United States Only)
Historic Aerials (United States Only)
CalTopo Maps (United States Only)